Wolf's mouth: etiology of the disease, anatomical features of the structure of the upper palate
The cleft of the sky, which in the circles far from medicine is called the cleft palate, belongs to the intrauterine pathologies of the craniofacial region of the skeleton. However, despite the visible external defects and difficulties faced by parents in caring for a child with a similar anomaly, the disease is quite successfully amenable to prompt correction at preschool age. And in the absence of other concomitant defects of development and compliance with the rules of rehabilitation, children do not lag behind their peers. And the cosmetic defects remaining after the intervention are completely fixable with the help of modern methods of plastic surgery.
The formation of the upper jaw occurs approximately in the second month of embryonic development from rudimentary gill arches, which are separated from each other by gill pockets. They are rich in blood vessels and nerve endings and contain the rudiments necessary for the further formation of bone and cartilage tissue.
The maxillary processes of the first branchial arch, fused together, form the upper jaw, certain structures of the face, including the upper lip. On the maxillary processes there are protrusions, which are called palatine, growing together, they form the sky. Violation of this process and leads to the emergence of such a congenital pathology, as the wolf's mouth.
The hard palate is located in the upper part of the mouth, each person can easily feel it, slightly raising the tongue. It consists of a solid bone plate and is covered with soft tissues. The main function of this structure is the separation of the oral and nasal cavities. In the middle there is a longitudinal hilly protrusion - the seam of the palate, which is formed during the intergrowth of the palatal processes during intrauterine development. According to it, the cleft of the sky passes in case of congenital pathology of the wolf's mouth.
The soft palate forms the back wall of the throat. At the heart of its structure are fibrous lamina, muscles attached to it, from the outside it is covered with multilayered epithelium. In the structure of the soft palate there is a palatine curtain, whose position is not constant. At rest, it, roughly speaking, “hangs down”, however, when swallowing saliva or food, it rises upwards, tightly separating the oral cavity from the nasopharynx. At the back edge of the soft palate is a hanging protrusion (uvula). This structure provides the promotion of chewed food from the mouth to the lower parts of the digestive tract, is involved in the implementation of speech and respiratory function.
According to the severity and pathophysiological characteristics of a congenital defect, the cleft palate is classified into:
- hidden, when the cleft covers only part of the soft palate, the bone structure and mucous membranes of the solid remain unchanged;
- incomplete, in which the splitting affects the soft palate entirely, and solid only partially;
- full when both soft and hard palate is affected;
- through one and two-sided, affects both parts of the upper palate and usually proceeds with the formation of a defect in the form of a “ cleft lip ”.
The emergence of this pathology is due to the influence of various factors on the process of fetal development. They can be divided into exogenous and endogenous.
Endogenous include:
- Mechanical pressure on the bone-facial skeleton of the fetus. This may be an excess amount of amniotic fluid, abdominal trauma, unsuccessful attempt to terminate a pregnancy (non-drug abortion).
- Exposure to excessive heat. Hyperthermia of the fetus may be due to heat stroke due to prolonged exposure to the sun, fever against the background of an infectious or viral disease. For the same reason, if pregnancy is suspected, it is necessary to refrain from visiting the bath, sauna, solarium.
- Radiation exposure . Danger may be living in a poor ecology area, working with radiographic medical equipment. Some doctors consider it dangerous and a long stay at the computer, but this hypothesis has not yet found scientific confirmation.
- Fetal hypoxia. Oxygen is necessary for the formation of any tissues and organs. Its inadequate supply with the bloodstream leads to a variety of developmental pathologies, which include the cleft palate. Risk factors for prenatal hypoxia are a strong decrease in the level of hemoglobin in the blood, marked toxicosis, accompanied by poor appetite and vomiting, in early pregnancy, cardiovascular and respiratory system pathologies. Impaired blood flow can occur in diseases of the uterus, viral infections, etc.
- Avitaminosis . A lack (as well as an excess) of vitamins can cause a disorder in the process of the formation of the internal structures of the fetus. In the early stages of childbearing, folic acid is especially needed.
- Exposure to toxins. It should be borne in mind that the usual cosmetic and disinfectants used every day can cause irreparable harm to the unborn child. Thus, a pregnant woman should refrain from using chlorine-based cleaning products. When choosing cosmetics, shampoos and conditioners, products containing such chemical compounds as alkylphenol ethoxylate, Accutane should be avoided. Especially dangerous for a pregnant woman are mercury, formaldehyde, nitric oxide, agents used for the treatment of agricultural plantations.
- Use of narcotic drugs.
- Smoking. It has been scientifically proven that this addiction increases the risk that a wolf's mouth will form by more than 50%.
- Acceptance of certain drugs. In the first trimester of pregnancy, almost all medications are contraindicated. Doctors recommend refraining from the use of most antibiotics, agents that affect the activity of the central nervous system, and thyroid hormones.
- Toxins produced by pathogenic flora. Particularly dangerous are certain viral infections, in particular, CMV, herpes, rubella, mumps, chickenpox and some others. Also, the risk of splitting the upper palate is increased if the woman suffers from chronic sexually transmitted diseases.
- The impact of stress factors. The release of adrenaline, norepinephrine and other biologically active substances into the bloodstream, which occurs during psycho-emotional stress adversely affects the fetal development of the fetus.
Endogenous, "internal" reasons for which the wolf's mouth appears, include gene mutations.
 According to medical statistics, if a mother or father was born with splitting of the upper palate, the risk of the appearance of the same pathology in a child is about 20%. The state of the germ cells also affects the intrauterine formation of organs and systems of the fetus. Long-term smoking, alcohol abuse, drug addiction negatively affect fertilization processes.
According to medical statistics, if a mother or father was born with splitting of the upper palate, the risk of the appearance of the same pathology in a child is about 20%. The state of the germ cells also affects the intrauterine formation of organs and systems of the fetus. Long-term smoking, alcohol abuse, drug addiction negatively affect fertilization processes.
Also, the risk of non-cleft of the upper palate increases with age. The exact mechanism of this violation is not yet known, but according to experts, the probability of pathology is higher if at the time of pregnancy a woman is older than 40 - 45 years, especially if this is the first child.
As a rule, the diagnosis of cleft palate can be made on the basis of the ultrasound results at 20 - 24 weeks of gestation. But the presence of this pathology is not an indication for termination of pregnancy, since the disease is quite amenable to correction by means of an operation using the method of uranoplasty or cycle plastic.
Wolf's mouth disease: the symptoms of various forms of pathology
According to the clinical picture, all forms of pathology have similar features.
Wolf's mouth disease is accompanied by the following disorders:
- Disorders of digestive function . The newborn is not able to eat normally, with severe lesions of the upper palate is almost impossible to establish breastfeeding. Doctors recommend the use of special nipples, however, even against the background of their use, the child gains weight more slowly, does not receive enough vitamins and nutrients in sufficient quantities.
- Respiratory disorders. Such disorders begin immediately after birth. Respiratory movements become shallow, superficial, so the child often suffers from hypoxia, anemia, and other disorders associated with lack of oxygen.
- Delayed speech development. The upper sky is involved in the pronunciation of many sounds, so its splitting is accompanied by pronounced speech therapy disorders.
- Predisposition to inflammation of the middle and inner ear. Changing the passage of air through the nasopharynx, food ingress into the nasal cavity leads to the development of an inflammatory process, reducing the activity of local immunity. Chronic pathology can cause persistent hearing loss.
The cleft of the soft palate is hidden when the gap is covered with epithelial membrane, and open, when the pathology covers all the tissues of a given structure. In addition, such a disease is classified as complete, in which non-invasion reaches the border of the hard palate and is accompanied by its underdevelopment, and incomplete, affecting only the muscular tissue of the soft palate. Wolf's mouth disease is usually accompanied by severe respiratory and swallowing disorders, and speech disorders.
Unilateral or bilateral cleft of the soft and hard palate may be hidden under the epithelial membrane, however, the pathologies associated with such a birth defect manifest as much as possible from the first days of a child's life.
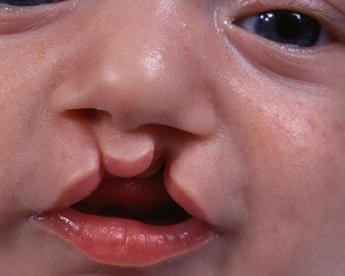
Unilateral cleft of the hard upper palate is accompanied by a violation of tightness between the oral and nasal cavity, which leads to a breakdown of the respiratory and digestive functions. In addition, the child can not pronounce all the sounds in the pronunciation of which the upper sky is involved. Often, a similar disease of the wolf's mouth is combined with a hare lip. Bilateral splitting of the upper palate is always accompanied by a cleft lip, it is difficult and requires surgical intervention as early as possible.
Wolf's mouth is detected near the end of the second trimester of pregnancy. However, ultrasound is not always informative. The child can cover his face with his hands, or his position in the uterus does not allow the doctor to conduct a detailed examination. Therefore, in case of doubt, re-ultrasound using a doppler is recommended.
Early diagnosis will allow parents to prepare for appropriate care for the newborn, to consult with experts. From the moment of birth, a child with a cleft palate requires close observation of pediatricians, control of respiratory function. However, the first surgical intervention (in some cases they will need several) is carried out not earlier than one year old.
Wolf lip: surgical correction of the defect
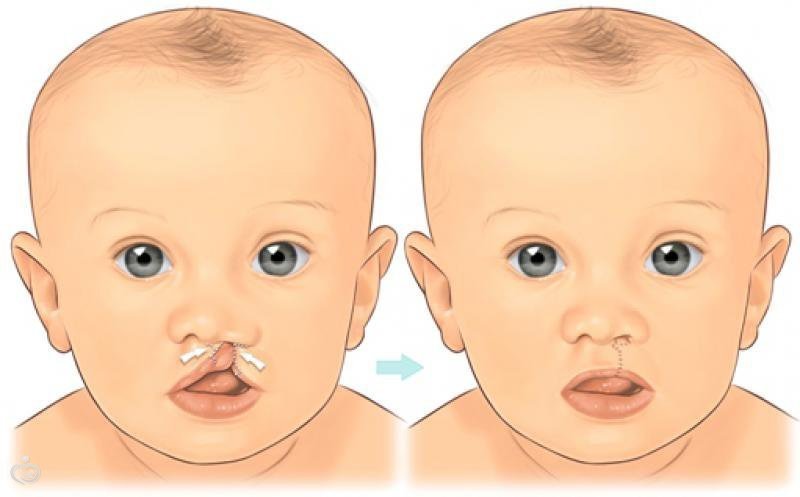
Usually the first question that parents of a child with a similar pathology ask a doctor is the age at which an operation can be performed to eliminate this defect. The answer depends on the severity of the defeat of the upper palate. If the pathology affects only the soft palate, surgery can be performed at the age of 12 to 24 months.
Correction of splitting of the hard palate is possible not earlier than 3 - 4 years. Otherwise, there is a high risk of impaired development of the facial skeleton. With bilateral lesions, two operations are necessary. They are carried out with an interval of 6 months.
Veloplasty is considered the most benign surgical intervention, but it is suitable only for the correction of the soft palate cleft. To correct the defect using their own areas of the mucous membrane of the nasopharynx and oral cavity. As a rule, the operation is well tolerated by young patients, and within a few days the child can return to the usual way of life and nutrition.
Correction of hard palate (uranoplasty) is a much more complicated surgical procedure. However, modern technologies allow not only to correct the defect, but also to fully restore the functions of the hard and soft palate. To eliminate the reaction of rejection, use patches of skin from the lateral surface of the cheeks and the upper palate.
Naturally, such an operation is not complete without the use of anesthesia. The best option is inhalation drugs, their introduction begin after intubation of the trachea and connecting the device. In some cases, for general anesthesia, drugs are used for intravenous administration, the most common today is Propofol. During the operation, the patient is under the constant supervision of an anesthesiologist, who controls the pulse, respiratory rhythm and other vital signs.
The rehabilitation period can last up to one and a half months. On the first day after surgery, edema and bleeding may occur at the suture site. To prevent obstruction of the respiratory tract of the child should be kept in the position on its side.
Important
To prevent infection, antibacterial drugs of a wide range of effectiveness are prescribed, analgesics must be prescribed.
When the wolf's lip is operated, the return to normal diet should be gradual. In the first few days, special nutrient solutions are administered intravenously to the patient. For the correct formation of the upper sky after the operation, a plate made according to individual measurements is installed. It is left for 1 - 1.5 months and removed for a meal and classes on the formation of correct speech.
After surgery, the child must consult an orthodontist and a dentist. Also required classes with a speech therapist. A specialist will write out a plan for independent study to parents. The simplest exercises are blowing bubbles in a glass of water through a cocktail tube, blowing balloons.
Also recommend:
- sticking the tongue out as much as possible, trying to reach the chin;
- inflate the cheeks, releasing the air alternately through the right and left corner of the lips;
- pronounce consonants with mouth tightly closed;
- various lip exercises;
- the game of "horse" (click language);
- drinking water in small portions;
- gargling.
But the wolf lip can not be corrected in a number of patients. Contraindications to surgical intervention are severe associated intrauterine developmental defects, cardiovascular and respiratory system pathologies, intolerance to drugs for anesthesia.
In some cases, the operation can lead to improper formation and development of soft palate tissues. If such disorders interfere with speech and digestive function, re-surgical intervention is recommended. Other complications usually occur with non-compliance with the advice of a physician. Possible divergence and infection of the seams, the formation of coarse scars.
In the vast majority of patients, the operation is well tolerated. Sometimes traces of the defect remain on the face, in which case it is necessary to contact a plastic surgeon who will eliminate them completely. After a complex of surgical measures, wolf lip and cleft palate do not affect the future life of the child.