Gynecomastia: clinical picture, diagnostic methods and classification of the disease
Gynecomastia is a disease with a complex polyeiological mechanism of development, manifested as a bilateral (much less often one-sided) enlargement of the mammary glands in men. Such changes occur due to hypertrophy of the glandular, connective and adipose tissue.
In accordance with the ICD N62 classification system generally accepted in medicine, the disease was first described in the second half of the 18th century, and the name comes from a combination of Latin terms “gynes”, which means “woman” and “mastos” - “breast”.
The development and further functioning of the mammary glands depends on the effects of a number of hormones: androgens, estrogens, somatotropic hormone, prolactin and pituitary gonadotropic hormone.
During fetal development, breast tissue is laid in children of both sexes. Further breast formation depends on the ratio of androgens and estrogens. With a high activity of the latter, the mammary glands develop in a female type and, accordingly, vice versa.
It is worth noting
In men at puberty, the ratio of testosterone and estradiol in the blood is 300: 1, respectively. Even minor deviations in the balance of "male" and "female" sex hormones towards androgens can cause active proliferation of glandular tissue at any age, which leads to the development of such diseases as gynecomastia.
Inactivation of steroid hormones occurs mainly in the liver, kidneys, to a lesser extent - in the intestine. In the liver, the inactive metabolites of these biological compounds break down into soluble substances and are eliminated by the kidneys in the urine. Part of the metabolites enter the intestine through the biliary tract and then re-enter the systemic circulation.
Therefore, theoretically, the pathology of any of the listed organs can cause a disturbance in the hormonal balance. However, most experts are inclined to believe that gynecomastia results from an increase in estrogen concentration.
They are formed from glucocorticoids under the influence of certain liver enzymes or androgens in the process of specific transformations in the peripheral tissue.
If we summarize all the current data on the etiology and pathogenesis of gynecomastia, we can identify the most likely causes of the disease.
It:
- tumor lesions of the mammary glands, with such pathologies, the level of estrogen does not exceed normal, but the number of receptors for estrogen increases;
- estrogen-secreting neoplasms, in particular, Leydig cell cancer, neoplasms producing human chorionic gonadotropin, pathologies of the adrenal cortex;
- obesity, in which there is an increased transformation of androgens into estrogens under the influence of tissue aromatase;
- the effects of large doses of drugs containing estrogens and other adrenal cortex hormones, drugs that affect DNA synthesis in breast cells (for example, drugs for the treatment of prostate cancer), by the way, gynecomastia is not uncommon among bodybuilders who sit on steroids for achievement of optimum result of trainings;
- secondary or primary dysfunction of the gonads, for example, Klinefelter syndrome, testicular inflammation, drug or surgical orchiectomy, prostatitis;
- changes in the concentration of globulin, which is characterized by the ability to bind sex hormones, such a condition arises in the pathology of the thyroid gland, liver, therapy with certain drugs (some diuretics, ACE inhibitors, sympatholytics, neuroleptics and antidepressants, cardiac glycosides, etc.);
- hereditary defects of estrogen and androgen receptors and organs of the reproductive system (in particular, hypogonadism, acromegaly).
The role of increased prolactin production in the pathogenesis of the growth of breast tissue has not yet been confirmed. Experts believe that an increase in the concentration of this hormone adversely affects the activity of gonadotropins, however, for many men diagnosed with gynecomastia, the level of prolactin remains within the normal range, and vice versa, hyperprolactinemia is not always accompanied by an increase in the size of the mammary glands in men.
It is worth noting
Approximately half of the patients cannot determine the exact cause of the disease. In this situation, idiopathic gynecomastia is diagnosed.
 The characteristics of the clinical symptoms of the pathology depend on the exact type of gynecomastia and stage. A typical manifestation is an increase in the size of the mammary gland, which is formed regardless of the age of the man.
The characteristics of the clinical symptoms of the pathology depend on the exact type of gynecomastia and stage. A typical manifestation is an increase in the size of the mammary gland, which is formed regardless of the age of the man.
In severe cases, tissue growth can reach 10 cm or more. It is important to distinguish pathological cell proliferation from excessive fat deposition. In the initial stages, the patient notes the tightness when wearing familiar clothes, but in severe cases, the growth of tissues can reach 10 cm or more. As a rule, such changes are noted on both sides.
It is worth noting
Breast cancer in men is quite rare, but one-sided gynecomastia, especially accompanied by the presence of nodal seals in the nipple, is an indication for further examination to exclude cancer.
Diagnosing gynecomastia begins with examining a patient. The doctor notes the general features of the constitution, especially overweight, palpation of the testicles and hypertrophied mammary glands.
In addition to the standard clinical blood test and determination of glucose level, the following indicators should be checked by laboratory (results are evaluated over time):
- testosterone and estradiol;
- luteinizing and follicle-stimulating hormone;
- prolactin;
- thyroid-stimulating hormone;
- human chorionic gonadotropin;
- α-fetoprotein;
- sex hormone binding globulin (in the laboratory research forms, this analysis denotes SSSG, GSPG, GSSG).
Additionally, tests are conducted to assess the functioning of the kidneys and liver. Also exclude severe systemic congenital and acquired pathologies, especially malignant neoplasms. Mandatory research is an ultrasound scrotum, prostate and breast glands. The latter allows you to accurately establish the proportion of glandular and adipose tissue. In addition, conduct mammography.
It is worth noting
If the results of the ultrasound examination are questionable, a biopsy of the breast tissue is prescribed.
If gynecomastia is assumed, they make an appointment with an endocrinologist, a urologist. In the future, as the results of diagnostic manipulations are received, the patient can be referred to a specialist (oncologist, therapist).
When classifying the disease, the following types of gynecomastia are distinguished:
- False (it is also called lipomastia or adiposomastia), characterized by the predominance of lipid tissue in the hypertrophied mammary gland.
- True, characterized by a large amount of glandular tissue. In turn, it is physiological, developing in newborns, adolescents, in adolescence and old age, and pathological.
Depending on the pathophysiological changes in the tissues of the mammary gland, gynecomastia can be diffuse and nodular. Also distinguish between single and bilateral lesions. Doctors note that the left-sided form of pathology is more common, and even with a bilateral view of the disease, the left breast is enlarged somewhat more.
In addition, according to the histological signs of gynecomastia is:
- parenchymal, accompanied by hypertrophy with the formation of lobules;
- interstitial, characterized by the proliferation of connective tissue with foci of fat deposition.
Depending on the severity of pathological changes, there are four degrees of gynecomastia:
- on the first note minimal violations;
- the second seal does not exceed the diameter of the areola;
- in the third, the size is compared with the areola of the nipple;
- in the fourth seal exceeds the diameter of the areola.
In the clinical course of gynecomastia there are several stages:
- developing (or proliferative), lasts up to six months, at this stage, with properly chosen conservative treatment, the pathological process may regress;
- intermediate, lasts up to 12 months, differs by further transformation of the glandular tissue;
- fibrous, this is the final stage at which drug therapy will not bring results, you can correct the situation with the help of an operation with further medical elimination of the cause of the disease.
Non-surgical treatment of gynecomastia is carried out with the help of anti-estrogens. In particular, Tamoxifen is indicated. The dosage is calculated individually, but in most cases it is 0.1 g twice a day. The effect of therapy with tablets containing testosterone, dihydrotestosterone is not currently proven. In the absence of concomitant disease, physiological gynecomastia usually resolves on its own.
It is worth noting
If there is no result from conservative treatment for 2 months, the patient is offered other methods to solve this problem.
Some prefer the treatment of gynecomastia at home according to the recipes of traditional healers.
The following remedies are recommended:
- Mix in equal proportions chopped ginseng root, yohimbe bark (these ingredients can be purchased at specialty stores or ordered online), bilobed ginkgo leaves and freshly cut oat grass. Take about 200 g of the mixture (about
20–30 tbsp), pour a liter of medicinal alcohol and leave for 14 days in the refrigerator. Take half a teaspoon3-4 times a day for8-12 weeks. - Mix ginseng, raspberry leaves and licorice root in a ratio of 3: 1: 1. Pour a tablespoon of half a liter of boiling water, insist, strain and drink throughout the day. The course of treatment is at least 12 weeks.
It is worth noting
Without prior diagnosis and examination, treating gynecomastia with folk remedies is dangerous. Therefore, before applying any non-traditional methods of therapy, it is better to consult a doctor.
Gynecomastia is often a reason to offer the patient surgery. First of all, it is purely cosmetic. A man with a similar diagnosis often experiences psychological discomfort, sexual maladjustment.
The operation is carried out in one of the following ways:
- subcutaneous mastectomy with preservation of the thoracic fascia and subcutaneous tissue, also shown in tumor processes;
- subcutaneous mastectomy in combination with the removal of excess adipose tissue, shown in the false form of the disease, while the surgeon transports up the nipple-alveolar complex to achieve an optimal aesthetic result;
- endoscopic mastectomy, shown in the initial stages of the pathological process.
Usually surgery is well tolerated. Full rehabilitation lasts a month (after this time, you can engage in physical labor without restrictions), but the length of stay in the hospital does not exceed 48 hours, and the hospital patient is given out for 7-10 days.
Doctors recommend surgery to abstain from:
- with physiological gynecomastia at an early age, when the probability of spontaneous regression is high;
- elderly patients, in whom recovery after surgery takes much longer, and the operation itself carries certain risks;
- with various contraindications to the procedure.
It is worth noting
Initially, it is necessary to eliminate the main reason why gynecomastia originated, and then to deal with cosmetic correction of the defect.
The prognosis of the disease primarily depends on its type. The physiological form disappears independently within several years without any interventions of the doctor. However, if we are talking about pathological gynecomastia, the outcome is determined by the severity of the underlying disease.
False and true gynecomastia: a brief description of these forms of pathology
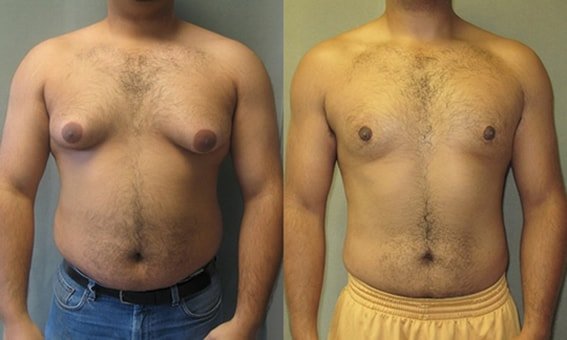 The type of gynecomastia can be determined after an ultrasound examination. The first type of gynecomastia (true) anatomically looks like hypertrophy of the glandular tissue in the breast area.
The type of gynecomastia can be determined after an ultrasound examination. The first type of gynecomastia (true) anatomically looks like hypertrophy of the glandular tissue in the breast area.
Lipid and fibrous tissue are presented in a minimum amount. Mixed gynecomastia type IIa is also accompanied by the proliferation of glandular structures (especially in the pectoral muscle), at the same time proliferation of connective tissue occurs. This form of the disease usually occurs while taking certain medications. Often, in addition to a pronounced increase in the size of the mammary gland, a transparent secret is secreted from the nipples.
In case of mixed gynecomastia of type IIb, glandular tissue proliferation is also noted, however, lipid deposits predominate in the structure of the hypertrophied breast.
Also for this type of pathology characteristic fibrous process. Usually accompanied by a change in the appearance of the nipple and the surrounding areola. The third type of the disease is false gynecomastia, which is also called lipomastia.
Pathophysiological features of this form of pathology is an increase in the size of the mammary gland due to lipid tissue. Usually accompanied by a change in body weight in a big way up to severe obesity. For the treatment of such a pathology, an operation is shown, which includes not only liposuction, but also a general correction of the appearance of the breast.
Although the surgery is quite complicated, the probability of complications is minimal, and the risk of relapse is absent with a corresponding correction of lifestyle and nutrition.
Gynecomastia in men: a pathological form of the disease
Pathological (true) form of the disease is a consequence of cancer tumors of various localization, endocrine disorders, systemic pathologies and taking a number of drugs.
So, gynecomastia in men, caused by a testosterone deficiency, can be triggered by the following diseases:
- Increased production of globulin. An important function of this biologically active compound is the binding of hormones in the liver. Therefore, an increase in the concentration of globulin inevitably leads to a decrease in testosterone levels.
- Secondary hypogonadism on the background of a decrease in the functional activity of the pituitary and hypothalamus. Due to the inhibition of the synthesis of pituitary gonadropine, the testes do not produce the required amount of testosterone, respectively, and the effect of estrogen on the breast tissue increases.
- Chronic renal failure. Experts have found that this pathology leads to a decrease in the secretory function of Leydig cells that produce testosterone. In this case, gynecomastia in men is combined with severe intoxication.
- Severe liver disease. Such diseases are accompanied by inhibition of androgen metabolism. As a result, the concentration of free testosterone in the blood decreases. At the same time, the inability of the liver to inactivate estrogen leads to its reverse flow through the bile ducts into the digestive tract and then into the systemic circulation.
The disease also occurs on the background of increased secretion of estrogen. However, an increased concentration of estradiol specifically affects the hypothalamic-pituitary system, thereby reducing the production of luteinizing hormone. This in turn leads to the inhibition of testosterone synthesis in Leydig cells in the testicles.
Gynecomastia in men on the background of increasing estrogen concentration is noted in such cases:
- Thyrotoxicosis. According to various sources, hypertrophy of breast tissue occurs in
10-40% of cases. Against the background of a malfunction of the thyroid gland, the conversion of androgens to peripheral tissue is enhanced, andandrostenedione synthesis in the adrenal cortex is also increased, which is further transformed into estrogens. - Klinefelter syndrome. Hereditary disease, accompanied by increased sensitivity of cellular receptors to estrogen. Often, gynecomastia in men is one of the first symptoms of pathology.
- Reyfenshteyn syndrome. It is also a genetic disorder characterized by increased estrogen production. In this case, an increase in the size of the mammary glands is noted in adolescence, and, unlike physiological gynecomastia, there is no regression of the pathology.
- A rare form of gynecomastia, due to increased activity of aromatase, under the influence of which there is a transformation of androgens into estrogens. In severe cases of this pathology, this process is accelerated 10 times.
- Congenital adrenal hypoplasia and other conditions associated with impaired steroidogenesis.
- Androgen secreting adrenal tumors stimulating the synthesis of androstenedione.
- Leydig cell tumor promoting estradiol production.
- Tumor, producing hCG (testicular germ cell tumors, carcinomas, regardless of location).
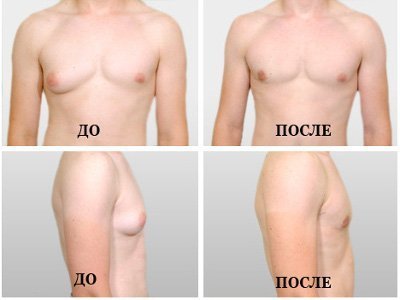 Gynecomastia in men may also develop on the background of prolactinomas and other intracranial lesions of the hypothalamic-pituitary system.
Gynecomastia in men may also develop on the background of prolactinomas and other intracranial lesions of the hypothalamic-pituitary system.
Such formations lead to an increased level of prolactin.
Such endocrine disruption causes so-called hyperprolactinemic hypogonadism. Stimulates the synthesis of prolactin and hypothyroidism. Often, gynecomastia in men develops on the background of long-term use of certain drugs.
The following medications are the most dangerous in terms of hypertrophy of breast tissue:
- estrogens and antiandrogenic agents (Proscar, Avodart, Androkur);
- calcium antagonists (especially Isoptin, to a lesser extent Adalat, Diltiazem);
- anticancer drugs (Paraktha, Aranoza, Alkeran, etc.);
- cardiac glycosides (Digoxin, Novodigal, Strofantin);
- H2 receptor blockers (Zanthac);
- ACE inhibitors (Capoten, Berlipril).
This is not a complete list of drugs that can cause such a complication as gynecomastia in men. However, other drugs (antidepressants, spironolactone, ketoconazole, etc.) are accompanied by a similar side effect in isolated cases. The disease is often the result of addiction to synthetic drugs.
It is worth noting
When it comes to possible complications, one should pay attention not only to the trade name of the drug, but also to the active substance. Other drugs with the same composition cause similar adverse reactions.
Gynecomastia: what it is in women, physiological gynecomastia in men and children
The disease, caused by age-related changes in hormonal levels, manifests itself in the form of a slight increase in the mammary glands .
The following types of physiological gynecomastia are distinguished:
- In newborns (neonatal gynecomastia). It develops under the influence of maternal estrogens entering the boy's body through the placenta. Lasts not for long, disappears spontaneously and does not require treatment.
- Teenage (juvenile or puberty). It is considered a variant of the norm. The peak of manifestation accounts for
13-14 years. Therapy is not carried out, since the pathological process stops independently after a while (usually in the period from six months to 3 years). Disease development is associated with an increased concentration of leptin, which stimulates the formation of estrogen in peripheral tissues.
It is worth noting
If the symptoms of gynecomastia occur at puberty, it is necessary to exclude endocrine pathologies. In the absence of any concomitant diseases, the patient's condition is constantly monitored using laboratory tests.
- In old age, up to 80% of physiological gynecomastia is recorded. Usually, the disease occurs in men after 50 years. The main cause of pathology is the relative excess of estrogen in the background of reduced testosterone production.
The development of gynecomastia in men can occur without changing the ratio of androgens and estrogens. One of the likely causes of such disorders is the increase in tissue sensitivity to estrogen. At the same time indicators of laboratory tests for a long time remain within the normal range. This form of the disease is called idiopathic. On Internet forums, many users ask the question: gynecomastia - what it is for women.
However, there is no need to look for photos and symptoms of this pathology in the open spaces of the network, since it simply does not exist. Hypertrophy of the breast tissue is possible only in the male. In women, a small breast augmentation is a physiological sign of pregnancy and premenstrual syndrome.
