How to do breast augmentation surgery and what are its benefits and disadvantages
Breast augmentation (or magnifying mammoplasty) is the most common procedure from the category of aesthetic surgery.
It helps to change and improve the shape of the mammary glands.
When asking how a breast augmentation surgery is performed from a patient, doctors first report that silicone gel implants, saline implants or, in some cases, subcutaneous fat are used for this.
Benefits of magnifying mammoplasty:
- It is a long-term solution to achieve the perfect figure.
- A woman will look better in clothes and a bathing suit.
- For many men, a woman with big breasts looks very attractive and desirable.
Minuses:
- Breast implants require medical supervision.
- Implants must ultimately be replaced.
- The usual surgical risks are present.
Who is a good candidate for breast augmentation:
- Those who believe that her breasts are too small and complex about this.
- Those who are shy to wear a swimsuit or fitted dresses with a deep neckline.
- Women whose breasts have changed shape and decreased after breastfeeding or weight loss.
- Those with one breast are noticeably smaller than the other.
note
Enlarged mammoplasty is suitable for healthy women with realistic expectations regarding this procedure.
It is important to choose a surgeon based on:
- Education, training and certificates available.
- Experience working with breast augmentation surgery.
- The level of patient comfort when dealing with the selected doctor.
- The patient should make sure that both the operation and the follow-up activities will be carried out by the same plastic surgeon.
- Price should never be a decisive factor when choosing a location for a breast augmentation surgery. Security should be number one priority. You should carefully read the reviews about the clinic and the doctor before agreeing to the operation.
To help detect and monitor any changes in the breast tissue, a plastic surgeon may recommend that the patient do a control x-ray examination of the mammary glands (mammography) before the operation.
Before the operation, it will be necessary to stop smoking, at least 6 weeks before the operation, so that the healing of the tissues goes better. Do not take aspirin and some anti-inflammatory drugs that may increase bleeding.
Do not eat or drink anything after midnight on the night before the operation and wear loose clothing, including a tight-fitting pitted bra after the operation. Regardless of the type of operation, hydration (hydration of the body) is very important before and after the operation.
If a procedure is planned with subcutaneous fat , the patient will be asked to wear a special bra to expand the skin and tissues around the breast in order to prepare them for fat injections.
How to do breast augmentation surgery? Breast augmentation is usually performed under general anesthesia. The whole process takes from 1 to 3 hours. The patient will stay in the hospital for 24 hours, after which she will be discharged home. After that, she will need to undergo a daily check-up at a plastic surgeon for 5 days.
How is breast augmentation surgery performed and who shouldn’t do it
 Breast augmentation is not recommended for women younger than 18 years, as their body shape can still change naturally.
Breast augmentation is not recommended for women younger than 18 years, as their body shape can still change naturally.
It is undesirable to do magnifying mammoplasty for women who have not yet given birth or breastfed. They may need additional surgery after cessation of lactation, due to changes in the shape of the breast.
You can not do mammaplasty women with fibroma, breast cancer, diabetes, tuberculosis and myocardial infarction .
Another contraindication is bleeding disorders.
Important
Increasing mammoplasty does not correct heavily sagging breasts.
Here is how breast augmentation surgery goes:
- The patient will be given a dose of intravenous antibiotics as a precaution. The doctor will mark with some surgical markers on the chest. This ensures proper placement of the implants and their symmetry after the operation.
- The patient is given anesthesia or local, while she is awake, and only painful sensations in the chest area are blocked, or general, by sinking into sleep. Most women undergo general magnoplasty under general anesthesia.
- The surgeon makes an incision, picks up breast tissue, creates a “pocket” in the chest area and places the implant in that pocket.
- An incision is made in one of the following areas:
- along the bottom of the chest;
- under the arm (axillary);
- around the nipple (periareolar).
- An additional option is autologous (own) fat transplantation, a process in which the surgeon removes the patient's own fat from the abdomen, thigh or side, processes it, and then injects it into the woman’s chest. This procedure is currently considered experimental.
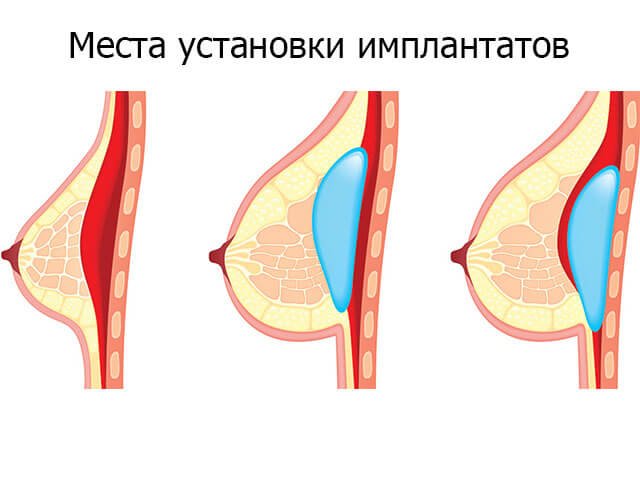
Many factors, including the patient's anatomy and the surgeon's recommendations, will determine the location of the implants. They will be under the pectoral muscle, located between the breast tissue and the chest wall or under the breast tissue, and on the upper part of the pectoral muscle.
It is worth noting
Placement of the implant under the pectoral muscle can distort the mammography results or make it impossible. Also, implants in this area impede breastfeeding.
What can be in case of unsuccessful breast augmentation surgery?
 After breast augmentation, the patient can return home on the same day after the operation, and within a week can start performing work that does not require physical effort. Energetic activities, such as sports and activities involving sharp hand movements, should be avoided for three to four weeks.
After breast augmentation, the patient can return home on the same day after the operation, and within a week can start performing work that does not require physical effort. Energetic activities, such as sports and activities involving sharp hand movements, should be avoided for three to four weeks.
The patient can return to all normal activities within three months after surgery. Common complications of a failed breast augmentation surgery may include:
- bleeding;
- hematoma;
- infection in the chest;
- adverse reactions to anesthesia.
Less common complications associated with unsuccessful breast augmentation surgery are deflation (rupture of the implant). With salt implants, this situation is usually completely obvious, because the effect of the increase is quickly lost in a day or two. Although physiological saline is absorbed by the body without harm, implant replacement must be performed within a few weeks to prevent overgrowth of the pocket.
Capsule contracture is a situation where a thick scar is formed around the implant (s). It can occur on one or both sides of the breast and can lead to a change in shape, discomfort in the mammary glands. Often occurs after infection or hematoma.
There are four types of capsular contracture:
- The breast is usually soft and looks natural.
- The chest is more firm to the touch, but it looks normal.
- The chest is hard and looks unnatural.
- The chest is heavy, quite often painful, and looks very unnatural.
25% of women will need another operation, 10 years after an increase mammoplasty, because implants do not "live" forever. Weight loss, pregnancy, and other factors may lead to the need for reoperation.
Women who have implants often choose not to breastfeed, so data on the effect of breast augmentation surgery on lactation are not enough. However, if an nipple areola incision was made during the operation, there is a small risk that minor ducts will be damaged and this can impede the ability to breastfeed. Women who have an axillary incision or an incision in the lower part of the breast can breastfeed without problems.
One of the unpleasant complications after unsuccessful breast augmentation surgery is loss of nipple sensation. It depends on a number of factors, including the shape of the breast and the type of surgery. In this case, the nipples will still respond to cold and stimulation.
While breast augmentation with implants does not increase the risk of developing cancer, foreign objects in the breast can interfere with mammography to detect suspicious formations.
