Breast reconstruction: when it is needed and how it is performed
 If a woman’s breast cancer treatment plan includes radical mastectomy (breast removal surgery), she will be offered a choice about what to do with missing breasts.
If a woman’s breast cancer treatment plan includes radical mastectomy (breast removal surgery), she will be offered a choice about what to do with missing breasts.
Some women prefer to live without one breast or use a prosthesis (put a false breast in a bra). Others prefer breast reconstruction.
What depends on the volume of plastic surgery for breast reconstruction
Breast reconstruction includes several different types of procedures with which surgeons try to restore the shape of the breast of patients undergoing mastectomy.
The specific type of reconstruction and its volume will depend on such factors as the age and type of the patient's body. Although breast reconstruction can not return to the woman those feelings that were before oncology, it gives a result very similar to a normal breast.
How can be removed
Breast reconstruction may be performed at the same time as mastectomy (immediate reconstruction), but this is not always possible. The advantages of immediate reconstruction include the presence of only one anesthetic, in addition the patient does not need to re-go to the hospital and there will be only one recovery period.
However, the recovery period will be longer than with mastectomy alone. And patients undergoing radiation therapy after mastectomy may have to wear a temporary implant for several months until anti-cancer treatment is completed.
If there are complications after reconstruction, this may delay the start of chemotherapy (if required). Reconstructive surgery may be performed some time after mastectomy. This is called slow recovery.
In this case, the woman will have more time to discuss options for breast reconstruction with the surgeon. In addition, breast cancer treatment will be completed and the reconstruction operation will not depend on it. Some time before the operation, she will have to wear a fake breast and the scar on the reconstructed breast will be larger than after immediate reconstruction.
How soft tissues are restored in the area of the removed breast
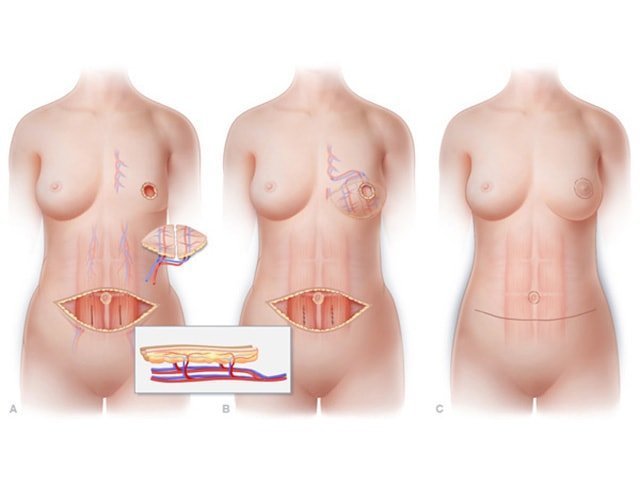
Breast reconstruction is usually divided into two categories: a procedure based on implants (expanders) or using autologous flaps (patient's own tissue).
Expander can be used
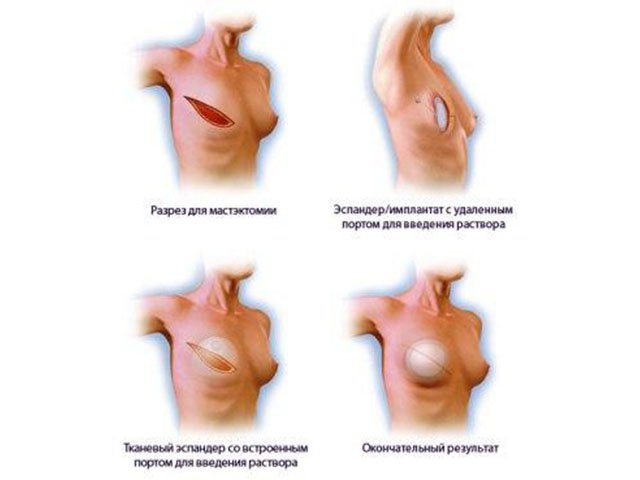
The basic principle of the method with an expander is to restore the lost amount of tissue through the expansion of the remaining skin of the breast and filling the shell of the breast with a permanent implant. This implant is filled with saline water (saline) or silicone.
The breast reconstruction surgery with an implant is shorter than with a skin-muscle flap reconstruction. The surgeon may suggest that a woman first use a temporary expandable implant. It allows the skin on the chest to stretch gradually. The expander will stay in the chest for three to six months. After the expanding implant reaches the desired size, the surgeon will replace it with a permanent silicone expander.
Sometimes it is possible to use a permanent silicone implant during the first operation. Sometimes implants need to be replaced after several years to preserve their appearance.
Skin and muscle graft transplantation
When breast reconstruction using a flap, donor tissue is taken from the back, abdomen, thighs or buttocks. It is formed under the skin to create a new chest. Tissue taken from the body gives a natural shape and feel of a reconstructed breast. Patchwork reconstruction is a more complicated operation than installing an expander and the patient will have to stay longer in the hospital. She will have scars in the places where the fabric was taken.
note
New breasts can change shape and size in the first few months. But after it takes a permanent form, the results are likely to be more durable than when reconstructed with an implant.
Combined technique
Some women with very large breasts may be recommended to combine patchwork with implant placement. In this case, a wide flap of skin and muscles from the back is taken. This is the standard method of breast reconstruction, which was first used in the
This flap is a source of soft tissue that can help create a more natural-looking form of the breast than an implant alone. Breast reconstruction is not prevention of recurrence of cancer.
Breast reconstruction after mastectomy: features of preparation, contraindications and postoperative complications
 After the breast has taken its final shape and size, the surgeon can perform a nipple reconstruction. This procedure involves removing a part of the nipple from a healthy breast and attaching it to a new breast. But most often the surgeon will form part of the skin on the new breast in the form of a nipple.
After the breast has taken its final shape and size, the surgeon can perform a nipple reconstruction. This procedure involves removing a part of the nipple from a healthy breast and attaching it to a new breast. But most often the surgeon will form part of the skin on the new breast in the form of a nipple.
To match the natural color, the new nipple and the area around it can be tattooed. This is usually done in a hospital.
Ways to restore the nipple-areola complex
Nipple reconstruction is an outpatient procedure and is performed under local anesthesia. Women who do not agree to a nipple reconstruction may prefer a silicone nipple. It is attached to the chest with a special glue and can remain in place for up to three months.
Nipple reconstruction is usually performed
Important
The reconstructed nipple does not respond to changes in temperature or touch and is not as sensitive as the natural nipple.
Correction of the second breast
It is important to consider the opposite breast when planning breast reconstruction after mastectomy. Some women prefer to leave healthy breasts intact, but many prefer to achieve symmetry with a reconstructed breast.
Depending on the needs of the patient, symmetry can be achieved by breast reduction, breast lift, or breast augmentation with an implant. A few months after breast reconstruction, you can do surgery on the opposite breast.
If a woman needs chemotherapy, surgery on the opposite breast can be done as soon as the blood counts return to normal. It usually takes about a month. For patients with breast reconstruction with an expander-expander, the surgeon may suggest implant placement in the other breast in order to achieve similarity of both breasts.
The nipple and areola will be reconstructed later, after the breast has become final. All these procedures are outpatient, and the recovery time takes up to 2 weeks. After changing the opposite breast, cancer screening should continue.
Contraindications
Relative medical (non-cancer related) contraindications for breast reconstruction include:
- Morbid obesity (body mass index [BMI] ≥40 kg / m2);
- The impossibility of quitting smoking.
Older age is not a contraindication for breast reconstruction after mastectomy.
Preparation for surgery
It is important to follow the instructions that the doctor gives the patient at the time of the preoperative appointment. These may include blood and urine tests, a chest x-ray and an ECG.
A woman will be asked to stop taking aspirin, as well as any blood thinners, drugs containing vitamin E and any non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, including those that contain ibuprofen.
Since pain medications tend to cause constipation, it is advisable to take a stool softener twice a day for several days before surgery. The patient will be able to recover faster from the surgery if she performs the following things before the surgery.
- Do not smoke. Smoking can damage the blood supply to the tissues. It may also increase the risk of getting an infection. If breast reconstruction after mastectomy involves the removal of tissue from the patient’s abdomen, smoking increases the risk of hernia.
- Watch for weight. There is an increased risk of complications from anesthesia if the woman is overweight. Therefore, complete women, it is desirable to visit a nutritionist who will tell you how to lose weight before surgery.
- Staying physically active, if the tissue is taken from the abdomen, it is useful to do squats to increase the elasticity of donor tissues. We must strive to do up to 30 squats a day (preferably in the morning). However, before starting a workout, you should discuss its feasibility with your doctor.
Breast reconstruction after mastectomy often involves more than one operation. The first creates the basis of a new breast. In subsequent procedures, the size of the implant is adjusted, and a new nipple and areola are created. The first stage of reconstruction is done using general anesthesia. In subsequent operations, only local anesthesia may be required.
According to reviews of the majority of patients, especially those who underwent bilateral breast reconstruction, they could not wear clothes over their heads for a while after the operation. Therefore, before the operation, it is desirable to purchase clothes with zippers or buttons in front.
Complications
Possible side effects of breast reconstruction after mastectomy include:
- bleeding;
- infections;
- poor healing of stitches;
- breast irregularity;
- necrosis of all or part of the transplanted tissue;
- risks associated with intolerance to anesthesia during anesthesia.
In addition, the patchwork operation includes the risk of partial or complete loss of the skin-muscle flap and loss of sensitivity at the donor site.
Important
The risk of these complications increases if the woman smokes, is overweight or suffers from serious diseases.
The use of implants carries the risk of a dense fibrous tissue compressing the implant (capsular contracture) and rupture of the implant around a foreign object in the female breast. Capsular contracture can be treated by surgical removal of scar tissue or removal of the implant (with or without subsequent replacement).
A woman is likely to feel fatigue and pain for a week or 2 after surgery with the installation of an expander, or longer after a patchwork operation.