Laser or scalpel otoplasty: difference of operation
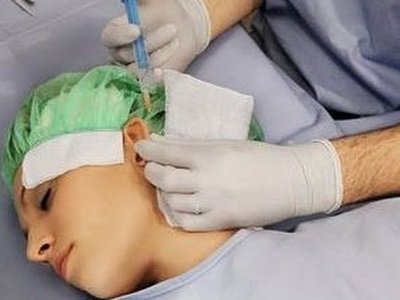 An operation on the ears to correct aesthetic defects is no longer surprising anyone. In modern plastic surgery, she occupies a leading position, along with rhinoplasty (operation on the nose). Highly qualified doctors and modern equipment allow you to do this procedure as quickly as possible, painlessly, and most importantly, successfully.
An operation on the ears to correct aesthetic defects is no longer surprising anyone. In modern plastic surgery, she occupies a leading position, along with rhinoplasty (operation on the nose). Highly qualified doctors and modern equipment allow you to do this procedure as quickly as possible, painlessly, and most importantly, successfully.
Traditional surgery involves the use of a scalpel. This surgical instrument for operations has been used for centuries. But today he has a powerful competitor - a laser beam, with the help of which many operations are performed on different parts of the human body, including on the ears. The appearance of an alternative raises a legitimate question: "Which is better otoplasty, laser or scalpel, the difference in what?".
In order to make it clear what is the difference between a scalpel and a laser, you need to decide on what unites them:
- indications for the correction of the auricle;
- target ear surgery;
- contraindications to otoplasty;
- preparation for surgery;
- methods of the correction procedure;
- recovery period.
Auricle correction is performed primarily for aesthetic purposes. An indication to it should be considered the client's desire to change the shape of the ears, if they do not look aesthetically pleasing. Another goal of otoplasty is to restore the missing parts of the auricle. This deficiency may occur due to abnormal ear development or injury to it by burns, frostbite, mechanical stress.
What corrects otoplasty:
- eliminates lop-earedness (removes hypertrophied cartilage tissue, forms an anti-scalp);
- improves the appearance of the auricle;
- reduces large ears (makrotiya);
- eliminates asymmetry;
- restores small, folded ears (microtia);
- restores or reduces the earlobe.
Contraindications to otoplasty are the same for any kind of surgical intervention. These include blood diseases, diseases of the endocrine system, infectious diseases, inflammation of the ears, exacerbation of chronic diseases, susceptibility to keloid scars.
If a patient with contraindications has an otoplasty, serious complications are possible. Therefore, surgery on the ears can be performed only after examination by a general practitioner and ENT doctor. Blood and urine tests are a must. Blood sampling is carried out for biochemical analysis, exclusion of AIDS and hepatitis, determination of blood clotting.
The course and methodology of the operation depends on the ear defect that needs to be fixed.
- The doctor conducts preliminary training: makes ear measurements and carries out computer simulations.
- Before making incisions, the surgeon makes a markup on the ear.
- Next, a scalpel or laser beam performs the necessary incisions, detaches the skin from the cartilage and corrects the auricle.
- If lop-earedness is eliminated, the operation is performed with a slit on the back of the ear, not far from the skin fold, while the cartilage is sutured, excised or removed.
- In the case of ear reduction, the incision is made in the front in the area of the curl fold and excess cartilage sections are cut out.
- Correction of the earlobe consists in stitching the tears or removing excess fatty tissue and skin.
- The operation lasts from 30 minutes to 2 hours.
 The recovery period is to follow a number of rules and care for the ear.
The recovery period is to follow a number of rules and care for the ear.
In the first week, you must wear a dressing for otoplasty and daily dressings.
Do not wet your ear or wash your hair before removing the stitches.
At least two months is prohibited to visit the pool and bath, play sports. Complete healing of the ear occurs after six months.
The main difference between scalpel and laser otoplasty is the following factors:
- laser surgery time is shorter than with classical surgery;
- blood loss with scalpel otoplasty is significant, and when using a scalpel are minimal;
- infection is eliminated by laser correction, while insufficient antiseptic in working with a scalpel can lead to serious inflammatory processes;
- after laser otoplasty, the soreness is minimal, and as a result of working with a scalpel, the ear hurts for a long time and severely;
- Laser correction of the auricle allows the ear to heal faster, and therefore reduces the recovery period.
What is performed otoplasty, laser or scalpel depends on the qualifications of the surgeon and the availability of modern equipment in the clinic. Plastic surgery centers equipped with the latest laser equipment can be found in almost all large and medium-sized cities of Russia: Voronezh, Chelyabinsk, Samara, Nizhny Novgorod, Yekaterinburg and many others.
Otoplasty with a scalpel and laser ear correction
Regardless of which tool is used for correction, the surgeon must master it. The master of his craft can feel the difference in the work of a scalpel and a laser beam. But this is also of interest to the patient, especially since the correction of the ears with a laser is considered a bloodless and painless operation. How does the work of the laser and the scalpel will take a closer look.
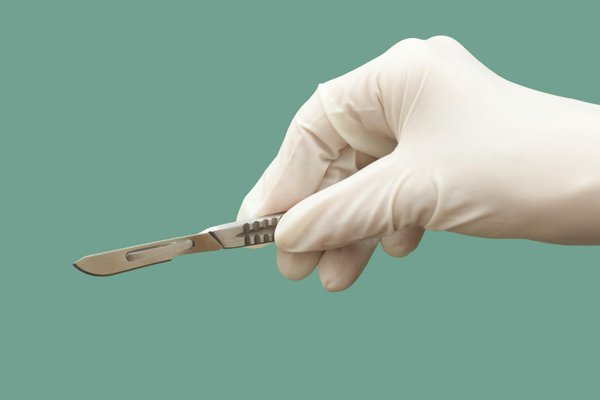
Scalpel Otoplasty: Instrument Features and Operations
A scalpel is a surgical knife made from medical stainless steel. It consists of a blade, a pointed tip and a handle. The purpose of the tool is the dissection of soft tissues during surgery. Depending on the purpose, scalpels can be of different sizes and odds.
When correcting the ears, the incision and work with the cartilage tissue occurs with a scalpel. First, an incision is made on the skin, then the skin tissue is removed from the cartilage. With this manipulation, blood flows abundantly from the wound, which must be periodically removed.
Working with cartilage often requires many small incisions along the lines of change, in other words, perforation of cartilage tissue occurs. This is painstaking work that requires precision movements of the surgeon and the fineness of the incisions.
Removal of excess cartilage is no less a responsible matter, since inaccuracy can adversely affect the result and lead to scarring. Otoplasty with a scalpel requires increased antiseptic working space. Since even minor contamination contributes to the penetration of infection into open wounds.
The disadvantages of scalpel ear correction are obvious:
- significant blood loss, abundantly flowing blood may accumulate under the skin and lead to such a complication as a hematoma, which can cause necrosis of cartilage;
- increased risk of wound infection and, as a consequence, complications such as perichondritis, otitis, inflammation and suppuration of soft tissues;
- long recovery period due to severe injury to the ear;
- the formation of scarring tissue as a result of inaccurate cuts.
Despite the flaws, the operation with a scalpel is quite safe and accurate.
In addition, infection during surgery is rare, and the skill of professional surgeons does not leave scars.
Laser otoplasty: instrument features and operations
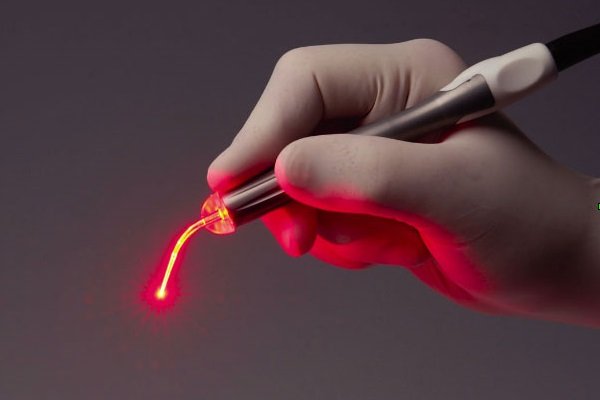 The laser for operations (laser scalpel) consists of two parts. In the stationary part is the generator of radiation itself and control units. The mobile part is a compact emitter connected to the main unit by a light guide. The laser beam is transmitted through the fiber to the emitter, through which the doctor performs the necessary manipulations. The radiation itself is transparent, which allows the surgeon to see the entire operated area.
The laser for operations (laser scalpel) consists of two parts. In the stationary part is the generator of radiation itself and control units. The mobile part is a compact emitter connected to the main unit by a light guide. The laser beam is transmitted through the fiber to the emitter, through which the doctor performs the necessary manipulations. The radiation itself is transparent, which allows the surgeon to see the entire operated area.
The tissue incisions with a laser scalpel are as thin as possible, since the effect of the beam on the operated area is limited to about 0.01 mm wide. At the site of exposure, the temperature of the tissues rises to about 400 degrees, as a result of which the skin area instantly burns and partially evaporates, that is, the proteins coagulate and the liquid passes into a gaseous state.
It is this reason that explains the minimum amount of blood during surgery and the impossibility of contracting an infection. The laser beam works very gently with the cartilage without damaging it beyond necessity. The edges are rounded and smooth, which allows you to accurately change the shape of the ear.
Optics laser has the following advantages:
- infection of tissues is excluded;
- the minimum amount of blood during and after surgery;
- there is a rapid tissue regeneration;
- the rehabilitation period is reduced;
- ears look as natural as possible (no scars).
Laser correction of the ears is gaining increasing popularity among the population. This method of surgery is recommended for the child, since after the laser exposure the pain is minimal and the ear heals faster. The cost of both scalpel and laser otoplasty varies in a significant range. It consists of various factors: the type of defect, the qualifications of the surgeon, the type of anesthesia, and many others. In order to determine the choice of the clinic, it is useful to read reviews on the Internet.
The price for laser otoplasty in Moscow is from 33,000 rubles, in St. Petersburg - from 30,000 rubles.