Hair Transplant Technology: Basic Transplantation Techniques
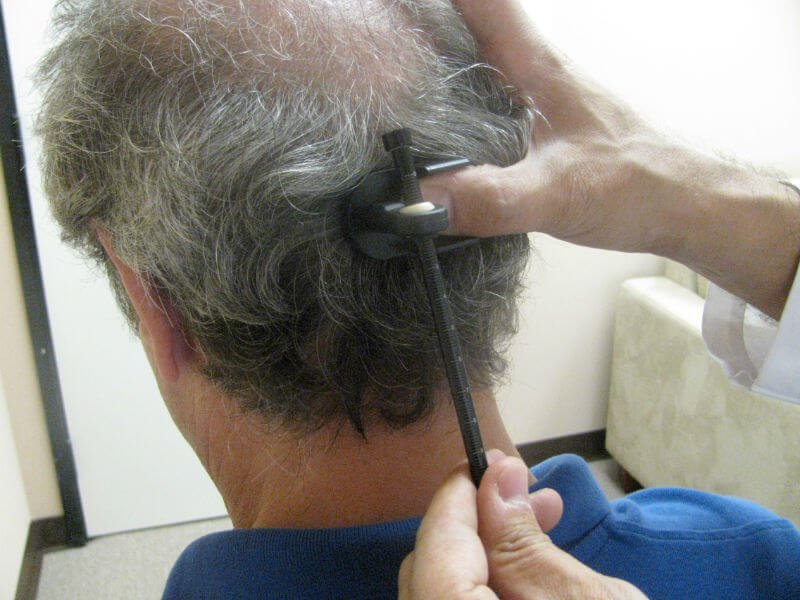 Various diseases of the scalp affect the condition of the hair in a negative way - dandruff may appear or even hair will fall out. With alopecia (loss of hair) a hair transplant can help.
Various diseases of the scalp affect the condition of the hair in a negative way - dandruff may appear or even hair will fall out. With alopecia (loss of hair) a hair transplant can help.
Age-related changes, diseases or external negative factors can affect the change in hair. In extreme cases, thinning of strands is observed, or even loss. This leads to bald patches and hairless areas. The parietal and temporal portions of the skull are much more frequently affected by such lesions. The way out, in this case, will be the technology of hair transplant from the occipital region to the damaged areas. Consider the thickness of the hair and the area affected by alopecia. Experienced experts will tell you in which cases the operation will be effective and will not bring harm.
Today, the following transplant methods are known:
- Classical. You can transplant hair with areas of the scalp. From a healthy part of the head, a part of the skin with hair follicles is cut off, and a similar piece of skin is removed in the damaged area. Next, insert a natural implant. All wounds are sewn up, but this is a painful process, after which there is a long recovery period. This method is rarely used.
- Follicular (seamless) - hair transplantation that leaves no wounds or stitches. The bottom line is to extract the follicles from healthy areas of the head and transplant to the affected parts. The doctor performs the operation using a special syringe, so it does not remain on the skin of the cuts. The main advantage of this method is a quick hair engraftment. However, there are contraindications. First of all, it is necessary to determine the causes of alopecia. If hair loss occurs unevenly and in different parts of the skin - then do not rush to the follicular method of recovery. The coat may continue to fall out from the now weakened part of the head (due to the transplanted follicles). First of all, it is necessary to determine the cause of the disease and eliminate it so that the transplant does not become a temporary solution to the problem. People of different ages suffer from androgenetic alopecia, and are adversely affected by radiation, sun, and salt water. A poorly balanced diet also leaves an unfavorable mark. Lack of nutrients in the body affects all organs (including hair can fall out).
Modern methods of hair transplantation
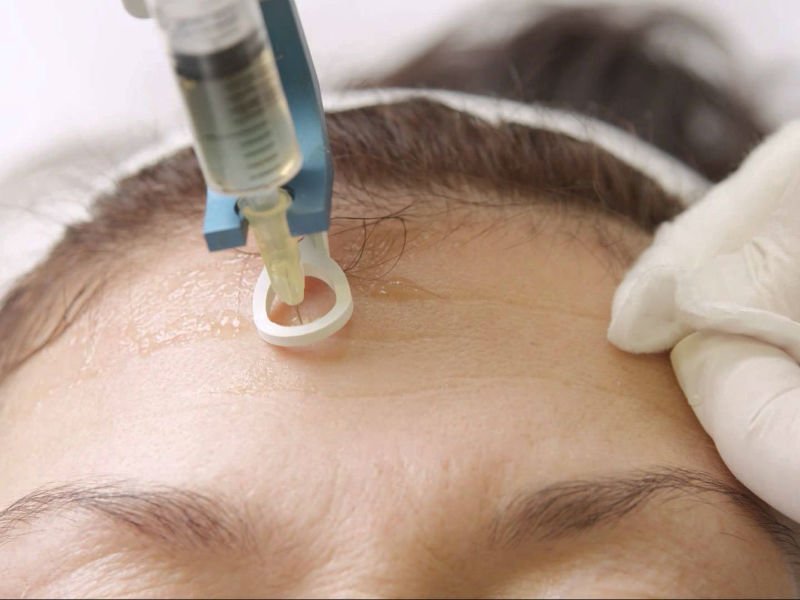 Let's look at popular methods of hair transplantation.
Let's look at popular methods of hair transplantation.
Seamless implantation (FUE - Follicular Unit Extraction) is the removal of part of the follicular groups from the donor area and their transplantation. With this method it is not necessary to dissect the donor flaps from the nape. The big advantage is that there is an even distribution of transplanted hair in the problem area.
The procedure does not injure the implantation zone or the area of donor material collection. The procedure uses “punchy” of different diameters from 0.75 to 1.0 mm. With their help is the taking of follicles. The doctor determines a graft consisting of
The grafts immediately move into the harvested pinholes in the recipient zone. Further recovery and regenerating period passes quickly and with almost no pain. Basically, grafts take root for up to 14 days. There are, of course, discomfort after the procedure, but they are eliminated by taking analgesic drugs. Return to the normal rhythm of life occurs in a week.
The procedure is outpatient and is carried out in several stages:
- Taking material from the donor.
- Creating holes in the recipient.
- Graft implantation to the donor.
Benefits:
- Seamless procedure.
- Absence of scar in the nape area.
- Hair transplant from another area of the body.
- Accuracy and prudence of grafts of appropriate structure and content of follicles.
Quilting —Strip mode. The bottom line is the simultaneous implantation of at least 5500 grafts or more at a time. The duration of the procedure is on average up to 5 hours. The operation is under local anesthesia.
Stages:
- Taking a flap from a donor area;
- Extraction of grafts from the taken area of the flap;
- Creation of microholes on the skin in the transplant zone.
After the procedure, the patient can go home, since he does not need to be in a hospital.
Graft implantation in pinholes
Stage I - taking the material from the donor. The surgeon produces a flap from the donor area (nape or temple). Special attention deserve:
- Skin turgor.
- The density of hair.
 Stage II - obtaining micrografts. Taken flap is formed on micrografts, consisting of
Stage II - obtaining micrografts. Taken flap is formed on micrografts, consisting of
Stage III - the creation of channels (holes) in the donor. Along with the preparation of grafts by assistants, the surgeon in parallel creates channels for the further implantation of grafts in the recipient area, taking into account the direction of hair growth.
Stage IV - implantation of micrografts. The transfer of grafts into the holes is carried out with the help of special surgical instruments (micro-tweezers). They minimize graft injuries during the procedure.
Transplantation of micrografts containing from 1 to 3 follicular hair creates naturalness and preserves the density of the implanted hair. Hair begins to grow after
Other methods of hair transplantation and recovery after surgery
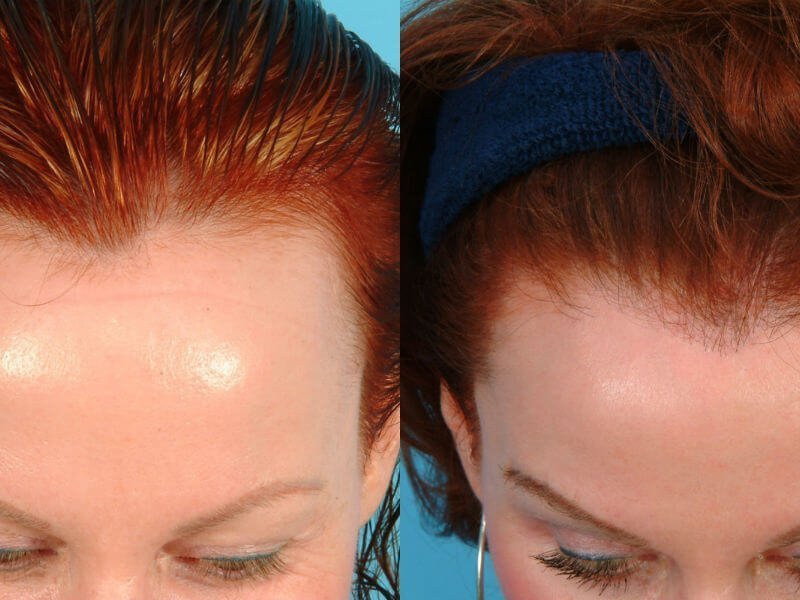 Prior to the active use of current methods, other surgical methods of hair transplantation were used. The painful area of skin with hair follicles was simply removed, and healthy areas of skin were sutured. Now this method is practically not used, even with small lesions.
Prior to the active use of current methods, other surgical methods of hair transplantation were used. The painful area of skin with hair follicles was simply removed, and healthy areas of skin were sutured. Now this method is practically not used, even with small lesions.
The method of transplantation of synthetic hair has several disadvantages. Artificial hair transplantation is performed : fibers are implanted onto the affected area with a special needle. Scars remain, and many patients noted itching in the damaged area after surgery. To all, further growth of hair does not occur, and they are prone to loss.
After hair transplantation with grafts (skin strips), sterile medical tissue is used to close wounds on the head. Usually, the stitches are removed after 2 weeks. Engraftment of hair can be done approximately 10 hours after surgery.
Should be a responsible approach to the choice of a specialist. His professionalism, experience and qualifications matter, because the result of transplantation depends on him. Perhaps for the desired result, you will need to repeat several operations.