Hip joint endoprosthetics: indications and contraindications for surgery, types of endoprostheses
The hip joint is one of the largest joints of the musculoskeletal system. Its structure provides mobility of the lower extremities and, as a result, body movement during walking, running, support and support during physical exertion (jumps, squats, weight lifting, etc.). Hip arthroplasty is a rather complicated operation, but in some cases it is the only way to restore the health and improve the quality of life of the patient.
In order to understand how the surgical procedure proceeds and to choose the optimal method for carrying out such a procedure, one should briefly highlight the anatomical structure of the hip joint. The main structural units of this joint is the head (proximal part) of the femur, which fits tightly into the acetabulum. It is located at the junction of the three pelvic bones that form it.
The articular acetabulum is lined from the inside with connective tissue, which is half a centimeter thick. In the central part this structure is covered with a synovial membrane. The shape of the acetabulum is fully consistent with the head of the femur and serves as a strong support for the lower extremities. Outside, the femoral head is covered with hyaline cartilage, with the exception of areas at the site of tendon attachment.
Below the head, the femur narrows, this section is called the neck, under which the body of the femur is located. On the border of these departments are large and small skewers. The fibrous bag of the hip joint consists of connective tissue fibers. They are located perpendicular to each other, which gives this structure additional resistance to heavy loads.
Outside the hip joint is covered with an articular capsule, but its density is not the same. It is more durable in the place of attachment of ligaments, which are attached on three sides and are called by the corresponding bone structures of the pelvic region. Also, the hip joint is surrounded by strong muscles that press the femur to the articular cavity and cover the back and bottom of the articular capsule. Due to the muscles, the main movements around the three main axes are ensured - bending and extension, adduction and abduction, rotation of the legs.
The blood supply to the hip joint is carried out by peripheral vessels extending from the arteries surrounding the femur bone. Nerve impulses are transmitted through the fibers - branches from the large sciatic, buttock, sex and some other nerves.
Important
In everyday life, the range of movement in the hip joint is much less potentially possible, which protects it from dislocations, injuries and other injuries.
Hip arthroplasty is a difficult operation, during which roughly the affected area is replaced with an artificial prosthesis. However, such surgery is carried out only under strict indications, when the possibilities of traditional conservative therapy are exhausted or do not bring the proper result.
Hip arthroplasty is necessary for the following diseases:
- unilateral or bilateral deformity of the connective tissue and its gradual replacement of the bone, such a pathology has been called deforming arthrosis or coxarthrosis, surgical intervention is recommended at stage II - III of the disease;
- coxarthrosis of the III degree in combination with pathological immobility (ankylosis) of one of the joints on the leg on the affected side;
- ankylosing spondylitis, which occurs with a lesion of the hip joints on both sides;
- necrotic changes in the cells of the femoral head as a result of trauma, disease, impaired blood flow, or other diseases; indications for surgery are necrosis of grade V-VI;
- posttraumatic degenerative changes of the hip joint (posttraumatic coxarthrosis) at stage III;
- fracture of the femoral neck in patients older than 65 - 70 years;
- abnormal mobility in the tubular portion of the femur (false joint) after 60 years;
- severe hip dysplasia, especially if such changes are congenital;
- cancer lesions of the connective tissue, including the growth of metastasis.
But even if there are indications for surgery, hip joint arthroplasty is not performed in such cases:
- the inability of the patient to move independently, even the restoration of the functional activity of the hip joint does not return the ability to walk to the disabled person, therefore, the extra risk associated with postoperative complications is not justified;
- serious pathology of the cardiovascular system, which makes it impossible to use anesthesia;
- blood clotting disorders or vice versa, the tendency to thrombosis, thrombophlebitis;
- respiratory failure;
- acute bacterial or non-infectious inflammation in the hip joint, endoprosthetics is carried out after the patient's condition is normalized;
- the presence of foci of purulent infection in the body, which increases the risk of sepsis and infection of the implant;
- paralysis on the side of the intended surgical intervention;
- disturbances of calcium metabolism, which manifests itself in the form of increased bone fragility (osteoporosis).
.jpg)
In addition, hip arthroplasty is recommended to be postponed until the skeleton is completely formed. Surgical intervention is not appropriate for severe obesity (the patient is recommended to lose weight, and then plan the operation). With caution, hip arthroplasty is done for endocrine pathologies.
Currently, two types of artificial implants are used to replace the affected joint, which differ in cost and on the principle of installation.
Depending on the prevalence of pathology, hip arthroplasty is performed using:
- Monopolar bipolar prostheses. They consist of a leg, neck and two heads, and the larger one corresponds to the size of its own acetabulum, which is not touched during the operation. But the disadvantages of such implants include the risk of further destruction of their own joint, which requires repeated surgical intervention.
- Bipolar total prostheses. Now they are used in virtually all operations to replace not only the neck and femoral head, but also the acetabulum. Such an implant is firmly fixed, suitable for all categories of patients, regardless of age.
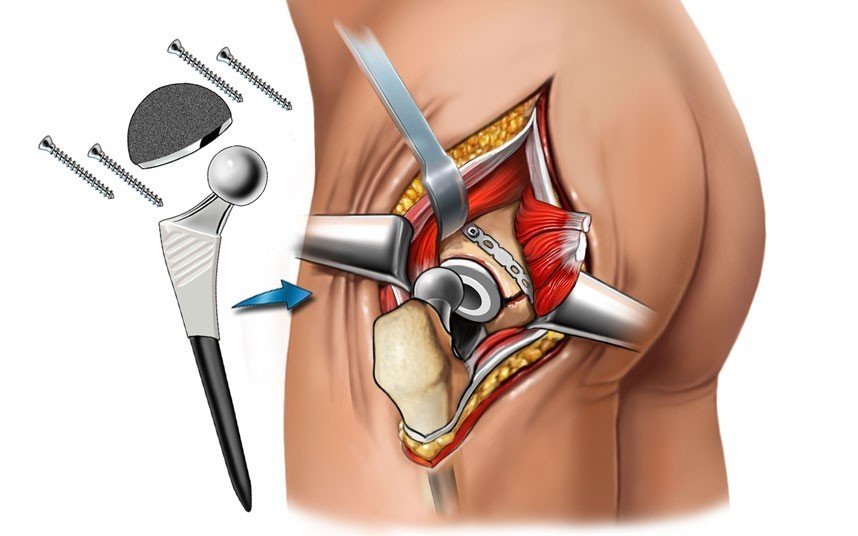
The prosthesis used consists of a cup, which is usually made of ceramics or polymers. It is installed in place of the affected acetabulum. The head of the prosthesis is also usually covered with a polymeric material, which greatly facilitates its movement inside the cup. The leg is made of durable metal (usually an alloy of cobalt and titanium), it performs the functions of the neck of the femur.
It is worth noting
The life of the implant depends on the materials that are used for its production. A quality prosthesis can last up to 20 years.
Rehabilitation after surgery is a long process. Rehabilitation activities necessarily include a complex of physical therapy (physical therapy), and the load on the affected limb should be minimal. Only functional movements are possible (contraction of muscles, later - walking with crutches, later - with a cane).
To prevent complications, it is necessary to use special bandages and liners , and rollers to reduce the load on the operated hip joint. Mandatory passive gymnastics (flexion and extension of the legs) with the help of medical personnel, therapeutic massage.
Subsequently, the patient is recommended physiotherapy , rehabilitation treatment in a specialized sanatorium. After surgery, you must follow a diet in order not to gain weight and prevent salt deposition and further deformation of the joint. If hip joint arthroplasty has passed without complications, the patient can return almost to the former way of life, to do exercises and some sports. But in the case of severe pathology of the connective tissue, endoprosthetic replacement of the hip joint will return the opportunity to independent movement, but it will not get rid of lameness.
But in some cases the operation does not go so smoothly. Possible complications are indicated by pain in the affected joint, swelling, fever. In such a situation, the doctor decides on re-operation to remove the prosthesis and advises a possible alternative to installing the implant.
Hip arthroplasty is an expensive procedure, especially if you use a high-quality durable implant. But at the present time it is possible to conduct a surgical intervention on a quota. You can read about what documents are required to receive a referral in the appropriate forum.
Revision hip replacement and other types of surgery, preparation and course of procedure
There are primary and revision hip arthroplasty. Primary, as the name implies, is carried out for the first time for certain medical conditions. Revision is intended to replace a worn out or damaged implant.
By the type of fixation, all modern prostheses are divided into:
- Cement attachment . For installation use a special adhesive solution, for the preparation of which biologically active materials are used. It firmly holds the implant in the bone tissue. This method of fixation is indicated for surgery in patients over 65 years of age, the presence of symptoms of osteoporosis. Also, cement attachment of implants is indicated for patients with a wide bone marrow cavity.
- Cementless fixing . This type of implant has many protrusions and holes. After its installation, its own bone tissue grows through them and thus fixes the prosthesis. Typically, these prostheses are recommended for patients younger than 55 years old with a well-developed bone base.
- Hybrid mounts . Similar implants have recently become widespread. For endoprosthetics of this type, the cup is fixed in a cementless manner in the acetabulum, and the leg of the prosthesis is cement.
.jpg)
Preparation for surgery involves several steps. The first step is to determine the functional length of the limb to compensate for the operation. To do this, make an x-ray of both hip joints and find out the correct position of the prosthesis.
The next stage of preoperative preparation includes determining the type of prosthesis and its fixation. It depends on the shape of the bone marrow cavity of the femur and the degree of joint damage. After selecting a specific implant, it is necessary to clarify the size of the components of the prosthesis.
Primary and revision hip joint endoprosthetics also includes a comprehensive examination of the patient. Consultation of a neurologist and a cardiologist, “standard” laboratory tests (biochemistry, blood and urine clinics, glucose tests, tests for specific diseases, etc.) are required. The anesthesiologist, for his part, also examines the patient to determine the exact drug for anesthesia and its dosage.
Course of operation
The patient is transported to the aseptic operating room and connect the equipment for supplying the drug for anesthesia. The course of the surgery and the correct installation of the prosthesis depends on the correct position of the patient during the procedure. The patient is placed on a healthy side, while the pelvis should be strictly perpendicular to the surface of the operating table.
Then the surgeon makes an incision up to 15 cm long, cuts through the muscle tissue to ensure free access to the affected area. After that, the articular capsule is excised and an osteotomy of the femoral neck is carried out, taking into account the previously obtained examination results. It is also necessary to prepare the inner surface of the acetabulum.
After these steps, the doctor first tries on a trial prosthesis to eliminate the presence of areas of instability in his position. If the surgeon is satisfied with everything, the implant cup is installed first. Then the bone marrow canal is drilled, and the cancellous bone tissue is removed from the upper part of the femur and the prosthesis stem is fixed. The wound is sutured in the usual way and install drainage for 1 to 2 days.
Primary or revision hip joint endoprosthetics should be performed with a qualified doctor in a proven clinic. It is better not to rely on reviews on the forums on the Internet, but to independently consult a few doctors. During a visit to the doctor, he can show a video of the operation, answer all questions of interest to the patient. Some patients go to foreign clinics, but in this case, the cost of the operation increases significantly.
Hip joint arthroplasty: possible complications, results of surgery, rehabilitation
.png)
Implant placement is a serious surgical procedure and, like any other abdominal surgery, carries a corresponding risk. During the procedure, there may be bleeding, an allergic reaction to injected drugs. With a tendency to thrombosis, doctors sometimes encounter a thromboembolism.
In the early postoperative period, some patients note bleeding from a wound, the formation of hematomas. Severe complications include suppuration of the suture, infection of the implant, its rejection and dislocation of the established prosthesis. The risk of undesirable complications increases with bilateral prosthetics in severe coxarthrosis, systemic lesions of the connective tissue, pathologies of the cardiovascular system and the respiratory tract.
After discharge of the patient from the hospital, there is a risk of deep scarring, which further limits the function of the hip joint. In addition, non-compliance with the recommendations of the doctor may cause early wear of the implant.
Hip arthroplasty is usually well tolerated. If the operation is carried out correctly, in young patients it is possible to almost completely restore the activity of this joint. However, intensive exercise and high loads on the joint are still impossible.
The first movements are possible already on the first day after hip joint arthroplasty was performed. Before removal of the drainage, flexion movements are allowed, to sit down in beds, to contract muscles. To activate the blood flow is useful breathing exercises.
After removal of the drainage tube, the patient is allowed to get out of bed, but only with the use of crutches. It is necessary to pay attention to the correct position of the legs to prevent dislocation of the prosthesis. With cement fixation of an implant with a cane, it is possible to move within 6 to 8 weeks; with the cementless method of fastening, this period increases to 3 months.
In the hospital, the patient remains for about 3 weeks. Despite the fact that the stitches are removed after 12 days, the rest of the time the patient and his relatives are taught the rules of rehabilitation, monitor the condition of the wound and the position of the prosthesis. To use special devices to reduce the load on the hip joint has to half.
But in the future, you must follow certain rules to prevent dislocation of the implant. It is strictly forbidden to sit on low chairs. Before turning, lay a special gasket between your knees. You also can not cross your legs in the prone position or sitting, sharply rotate the body, leaving the lower part of the body fixed.
Hip arthroplasty is often the only way to return to normal life and restore the functional activity of the lower limbs. Thanks to the technique of conducting the operation, the risk of complications is small. However, such a surgical procedure is not performed at an early age (up to 18 years old), even under strict indications.
More information about the features of operations on the joints and further recovery can be obtained from the company Artusmed .